The working principle of an ETP plant involves treating wastewater through physical, chemical, and biological processes. ETPs remove pollutants before releasing water back into the environment.
An Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) plays a crucial role in managing and treating industrial wastewater. By utilizing various treatment methods, ETPs help in reducing harmful contaminants present in the effluent. This process ensures that the discharged water meets environmental standards and is safe for ecosystems.
Understanding the working principle of an ETP plant is essential for industries looking to minimize their environmental impact and comply with regulations. Let’s delve deeper into how ETP plants function and their significance in wastewater treatment processes.
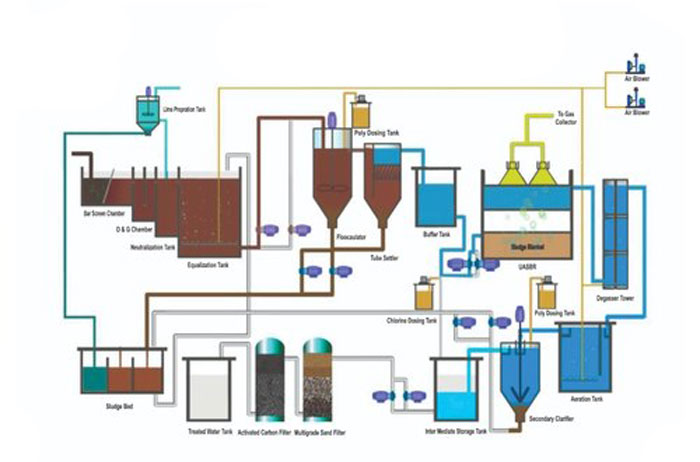
Credit: www.netsolwater.com
Introduction To Etp Plants
ETP plants based on the principle of treating wastewater through a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes. These plants efficiently remove contaminants to ensure the safe discharge of treated water back into the environment.
The Role Of Etp In Industrial Waste Management
ETP, or Effluent Treatment Plant, plays a crucial role in the management of industrial waste.
The main objective of an ETP is to ensure that the treated effluent meets the regulatory standards set by environmental authorities. An ETP works by employing various physical, chemical, and biological processes to treat the wastewater. These processes help in removing pollutants such as suspended solids, organic matter, heavy metals, and toxic substances, making the effluent safe for disposal or reuse.
By effectively treating industrial wastewater, ETPs help prevent the pollution of water bodies, soil, and air. They play a crucial role in safeguarding the environment and promoting sustainable industrial practices.
Importance Of Understanding Etp Mechanisms
Understanding the mechanisms of an ETP is essential for both industrial operators and environmental professionals. It allows them to effectively operate and maintain the treatment plant, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with environmental regulations.
By comprehending the working principles of an ETP, operators can identify any issues or malfunctions in the treatment process. This enables them to take corrective measures promptly, preventing any potential harm to the environment. Moreover, understanding ETP mechanisms helps in optimizing the treatment process, leading to improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
It allows operators to make informed decisions regarding the selection and dosage of chemicals, the control of process parameters, and the monitoring of effluent quality. Overall, a sound understanding of ETP mechanisms is crucial for effective waste management and environmental protection.
Fundamentals Of Etp Functioning
An Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) operates by treating industrial wastewater before releasing it into the environment.
Basic Components Of An Etp
- Tank for holding wastewater
- Screening mechanism to remove large debris
- Primary treatment unit for physical separation
- Secondary treatment unit for biological processes
- Tertiary treatment for further purification
Types Of Waste Treated By Etps
- Organic waste
- Chemical waste
- Biological waste
- Physical waste
Preliminary Treatment Stages
In an ETP plant, the preliminary treatment stages are vital for efficient wastewater treatment.
Screening And Grit Removal
- Screening removes large objects like plastic and paper from wastewater.
- Grit removal eliminates heavy particles such as sand and gravel.
- Prevents damage to downstream equipment.
Flow Equalization Techniques
- Equalizes flow rates to avoid overload on the treatment system.
- Helps in maintaining consistent wastewater quality.
- Reduces shock loads and fluctuations in the treatment process.

Credit: m.youtube.com
Primary Treatment Processes
In the primary treatment processes of an ETP plant, physical methods like screening and sedimentation are employed. These processes remove larger solids and pollutants before the water undergoes further treatment. This initial step sets the foundation for effective wastewater treatment.
Sedimentation Basics
Sedimentation is a key primary treatment process in an ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant). It involves the separation of solid particles from wastewater through the force of gravity. When wastewater enters the sedimentation tank, it is allowed to settle, allowing the heavier particles to sink to the bottom.
The settled particles, also known as sludge, are then removed from the tank, while the clarified water is collected for further treatment. During the sedimentation process, the wastewater flows at a slow velocity, allowing sufficient time for the particles to settle.
The tank is designed with a large surface area to facilitate the settling process. Additionally, baffle walls are installed within the tank to prevent the disturbance of settled particles by the incoming flow. The settled sludge at the bottom of the tank is periodically removed using mechanisms such as scrapers or sludge pumps. This sludge can then be further treated or disposed of properly according to environmental regulations.
Oil And Grease Separation
One of the primary concerns in wastewater treatment is the removal of oil and grease. These substances can be found in industrial effluents and can cause significant environmental damage if not properly removed. The ETP employs various methods to separate oil and grease from the wastewater. One common method is the use of an oil and grease trap or interceptor. This device is installed in the wastewater flow path and is designed to capture and separate the oil and grease.
The trap operates on the principle of density difference, where the lighter oil and grease rise to the top, forming a layer that can be easily skimmed off. The remaining wastewater, which is now free from oil and grease, continues to the next treatment stage. Another method used for oil and grease separation is the use of dissolved air flotation (DAF).
In this process, air is introduced into the wastewater, creating tiny air bubbles. These bubbles attach themselves to the oil and grease particles, causing them to float to the surface. The floating particles are then skimmed off, leaving behind clarified water.
It is important to effectively remove oil and grease from wastewater as they can interfere with subsequent treatment processes and have harmful effects on the environment. By employing proper oil and grease separation techniques, an ETP can ensure the effective treatment of industrial wastewater before it is discharged.
Secondary Treatment: The Biological Phase
Secondary treatment is a crucial phase in the working principle of an ETP plant. During this stage, the biological processes take center stage, playing a key role in removing contaminants from the wastewater.
Aerobic Vs. Anaerobic Processes
In the secondary treatment phase, both aerobic and anaerobic processes are employed to break down organic matter in the wastewater. Aerobic processes involve the use of oxygen, while anaerobic processes occur in the absence of oxygen.
Activated Sludge Process
One of the most common methods used in the biological phase is the activated sludge process. This method involves the use of microorganisms to consume organic pollutants in the wastewater, creating a sludge that settles and separates from the treated water.
Tertiary Treatment: Polishing The Effluent
Tertiary treatment is the final stage in the wastewater treatment process, where the effluent from the secondary treatment undergoes further purification to remove any remaining impurities.
This stage is crucial for ensuring that the treated water meets the required quality standards before it is discharged back into the environment. The tertiary treatment process, also known as polishing, employs advanced filtration methods, disinfection, and pH adjustment to achieve the desired level of water purity.
Advanced Filtration Methods
In the tertiary treatment stage, advanced filtration methods such as microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis are utilized to remove fine particles, dissolved solids, and organic matter from the effluent. These filtration techniques effectively capture even the smallest contaminants, resulting in significantly cleaner water that is ready for further purification.
Disinfection And Ph Adjustment
Additionally, pH adjustment is carried out to neutralize the acidity or alkalinity of the water, creating optimal conditions for the subsequent disinfection process and ensuring the treated water’s stability.
Sludge Handling And Disposal
Sludge handling and disposal are critical aspects of the working principle of an ETP plant. The plant efficiently manages the treatment process, ensuring effective removal and disposal of sludge to maintain a clean and sustainable environment.
Sludge handling and disposal is an essential process in ETP plant working principle. Sludge, which is a semi-solid residue, is generated as a byproduct of wastewater treatment. The sludge handling and disposal process involves the separation of water from the sludge, followed by safe disposal. In this article, we will discuss the sludge handling and disposal process, including sludge dewatering techniques and safe disposal methods.
Sludge Dewatering Techniques
Sludge dewatering is the process of separating water from the sludge to reduce its volume and weight. There are several sludge dewatering techniques used in ETP plants, including:
- Centrifugation: This technique involves spinning the sludge at high speeds to separate the water from the solids.
- Belt Press: This technique involves squeezing the sludge between two belts to remove the water.
- Filter Press: This technique uses a series of plates and frames to separate the water from the solids.
Safe Disposal Methods
After the sludge is dewatered, it is essential to dispose of it safely. The safe disposal of sludge is critical to prevent environmental pollution. Some of the safe disposal methods used in ETP plants include:
- Land Application: This method involves applying the sludge to agricultural land to improve soil fertility.
- Incineration: This method involves burning the sludge at high temperatures to reduce its volume and weight.
- Landfill: This method involves burying the sludge in a landfill site designed for hazardous waste.
In conclusion, sludge handling and disposal is an essential process in ETP plant working principle.
Monitoring And Control Systems
Monitoring and control systems play a crucial role in the working principle of ETP plants. By continuously tracking and regulating various parameters such as flow rates, pH levels, and chemical dosing, these systems ensure efficient and environmentally friendly operation. This real-time oversight helps maintain optimal performance and compliance with regulatory standards.
Automation In Etps
Automation in ETPs has made the monitoring and control systems more efficient and reliable. The control systems allow operators to monitor the functioning of the ETP plant in real-time, detect faults, and make necessary adjustments. Automation in ETPs has also reduced the need for manual intervention, making the process more accurate and less prone to errors.
Quality Control Checks
Quality control checks are an important aspect of the monitoring and control systems in ETP plants. These checks ensure that the water quality meets the required standards and is safe for discharge. Quality control checks include monitoring the pH levels, dissolved oxygen levels, and the presence of contaminants such as heavy metals and organic compounds.
Remote Monitoring And Control
Remote monitoring and control systems have made it possible to monitor and control ETP plants from a central location. These systems allow operators to monitor the functioning of the plant, detect faults, and make necessary adjustments from a remote location.
Data Management
Data management is an important aspect of the monitoring and control systems in ETP plants.Monitoring and control systems are an essential component of ETP plant working principle.
Automation, quality control checks, remote monitoring and control, and data management are some of the key features of these systems. These systems ensure that the water quality meets the required standards and is safe for discharge, while also making the process more efficient and cost-effective.
Etp Performance Optimization
When it comes to ETP performance optimization, it is crucial to implement effective maintenance strategies, consider upgrading and scaling ETP systems to meet increasing demands.
Maintenance Strategies
Implement proactive maintenance schedules. Regularly inspect and clean equipment. Train staff on proper maintenance procedures. Conduct frequent performance audits.
Upgrading And Scaling Etp Systems
Assess current capacity and future needs. Consider advanced treatment technologies. Upgrade equipment for improved efficiency. Expand treatment capacity as needed.
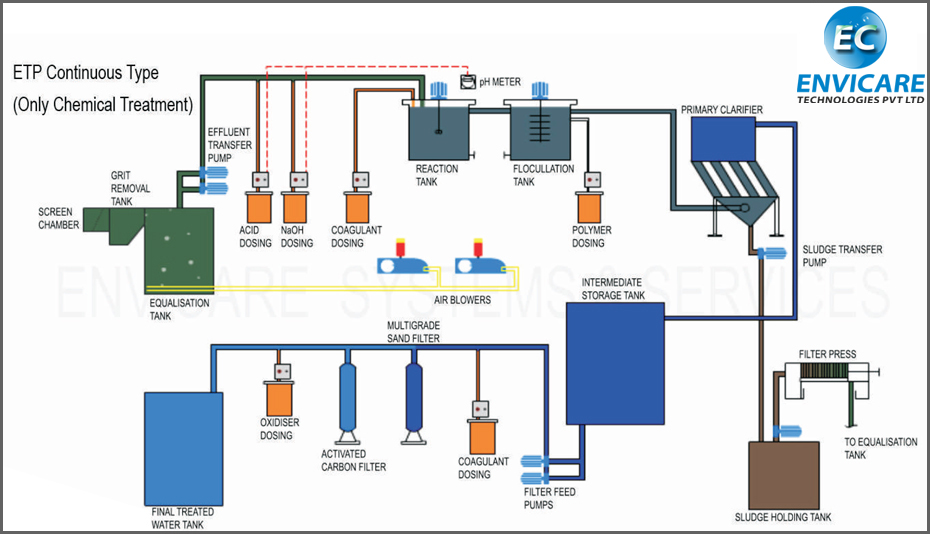
Credit: www.envicaresystems.com
Environmental Impact And Sustainability
Etp’s Role In Environmental Protection
The ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant) plays a crucial role in safeguarding the environment by treating industrial wastewater before releasing it into the ecosystem. It efficiently removes harmful pollutants and contaminants, preventing environmental degradation and protecting aquatic life.
Advancements Towards Sustainable Etps
Advancements in technology and innovation have led to the development of sustainable ETPs, which prioritize eco-friendly processes and reduce the environmental impact of wastewater treatment. These advancements focus on minimizing energy consumption, utilizing eco-friendly chemicals, and implementing advanced treatment methods to ensure the sustainability of ETP operations.
Case Studies
Case studies are effective ways to showcase the working principle of an ETP plant. By analyzing real-life scenarios, one can gain a better understanding of the various processes involved in treating wastewater and how these plants operate.
Case studies play a crucial role in understanding the working principle of ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant). They provide real-life examples of successful implementations and valuable lessons learned from failures. By examining these case studies, we can gain insights into the challenges faced, solutions implemented, and the overall impact of ETPs in different industries.
Successful Etp Implementations
Implementing an ETP successfully requires careful planning, proper design, and efficient operation. Here are some noteworthy case studies showcasing successful ETP implementations:
- Textile Industry: A textile factory in India significantly reduced its environmental impact by implementing an ETP. By treating and reusing wastewater, the company not only complied with regulatory standards but also saved substantial amounts of water, reducing their overall operational costs.
- Food Processing Plant: A large food processing plant in the United States implemented an ETP to treat its effluent. The plant successfully removed harmful contaminants from the wastewater, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and enhancing their reputation as an environmentally responsible company.
- Chemical Manufacturing: A chemical manufacturing company in Europe installed an advanced ETP system to address their wastewater treatment needs. This implementation not only helped them meet strict discharge limits but also led to improved water quality in the surrounding area, benefiting the local ecosystem.
Lessons Learned From Etp Failures
Learning from failures is equally important when it comes to ETP implementations. By understanding the reasons behind these failures, we can avoid similar pitfalls and ensure the success of future projects.
- Inadequate Design: In one case, an ETP failed due to improper design, leading to inefficient treatment and discharge of untreated effluent. This emphasizes the need for thorough engineering analysis and design to ensure the ETP meets the specific requirements of the industry and local regulations.
- Lack of Maintenance: Another case study highlighted the importance of regular maintenance and monitoring. Neglecting routine maintenance tasks resulted in the deterioration of the ETP’s performance, ultimately leading to non-compliance and penalties.
- Insufficient Training: A common factor contributing to ETP failures is a lack of proper training for the operators. Inadequate knowledge and understanding of the equipment and processes can lead to operational errors, compromising the effectiveness of the ETP.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Etp And How It Works?
It tracks an underlying asset like stocks or commodities. Investors buy and sell ETPs throughout the trading day, providing liquidity and price transparency.
What Is The Chemical Process Of Etp Plant?
The chemical process of an ETP plant involves treating wastewater with chemicals to remove pollutants.
What Is The Purpose Of The Etp Plant?
The purpose of an ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant) is to treat wastewater from industries and domestic sources. It removes pollutants and contaminants to make the water safe for discharge into the environment or reuse. The ETP plant helps to prevent water pollution and maintain the ecological balance of water bodies.
What Is The Physical Mechanism Of Etp?
The physical mechanism of ETP involves the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, leading to blood clot formation.
Conclusion
The ETP plant is an essential aspect of wastewater treatment in numerous industries. The working principle of ETP is based on various physical, biological, and chemical processes that help to remove contaminants from wastewater. The efficiency of ETP depends on several factors such as design, maintenance, and operation.
It is crucial to ensure that ETP operates effectively and efficiently to minimize the environmental impact of wastewater discharge. Therefore, industries must invest in advanced technologies and skilled personnel to manage and operate ETP plants effectively.
