Mild heat stroke symptoms, according to the NHS, include headache, dizziness, confusion, and nausea. Heat exhaustion can progress to heat stroke if not treated promptly.
Heat stroke is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. It can be life-threatening if not addressed promptly. Knowing the symptoms and taking appropriate action can help prevent serious complications. Heat stroke can occur when the body’s temperature regulation fails due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
In this blog post, we will discuss the symptoms of mild heat stroke, how to differentiate it from heat exhaustion, and what steps to take if you or someone else experiences these symptoms. It is essential to stay informed and prepared, especially during hot weather, to avoid heat-related illnesses.
Credit: www.nhs.uk
Recognizing Mild Heat Stroke
Recognizing mild heat stroke symptoms is crucial for preventing serious health complications. According to NHS, common signs of mild heat stroke include headache, dizziness, nausea, and excessive sweating. It is important to take immediate action by moving to a cooler place, drinking plenty of fluids, and resting.
Recognizing Mild Heat Stroke Initial Symptoms to Watch For When exposed to hot temperatures, the body may struggle to regulate its internal temperature, leading to mild heat stroke. It’s crucial to recognize the initial symptoms to prevent escalation. Common signs include headache, dizziness, and muscle cramps. Additionally, individuals may experience excessive sweating, rapid heartbeat, and flushed skin. These indicators signal the onset of mild heat stroke and should be promptly addressed. When to Seek Medical Attention If initial symptoms persist despite efforts to cool down, seek medical attention promptly.
Persistent headache, nausea, and vomiting may indicate a worsening condition. Furthermore, confusion, fainting, or a body temperature exceeding 104°F warrants immediate medical intervention. Prompt action can prevent mild heat stroke from progressing to a more severe state. Heat stroke symptoms should never be ignored, as they can rapidly escalate and pose serious health risks. Recognizing the initial signs and knowing when to seek medical attention are crucial steps in managing mild heat stroke effectively.
Body’s Response To Heat
When the body is exposed to high temperatures, it responds in various ways to cope with the heat. Understanding the body’s response to heat is crucial in recognizing and preventing heat-related illnesses. Let’s delve into the physiology of heat stress and how the body adapts to high temperatures.
Physiology Of Heat Stress
The body’s response to heat involves a complex interplay of physiological mechanisms. When exposed to high temperatures, the body initiates a series of responses to maintain its core temperature within a normal range. Blood vessels dilate to release heat and perspiration increases to facilitate evaporative cooling. These responses are orchestrated by the hypothalamus, a region of the brain that acts as the body’s thermostat.
Adapting To High Temperatures
Over time, the body can adapt to high temperatures through a process known as acclimatization. During acclimatization, the body becomes more efficient at sweating and cooling itself. Additionally, the heart rate may decrease during exercise in the heat, and there is an increased blood flow to the skin for improved heat dissipation.
Risk Factors For Heat Stroke
Heat stroke can be caused by various risk factors, such as prolonged exposure to high temperatures, physical exertion in hot environments, and dehydration. It is important to recognize the mild symptoms of heat stroke and seek medical attention promptly to prevent further complications.
Risk Factors for Heat Stroke Heat stroke is a serious condition that occurs when the body overheats and is unable to regulate its temperature. While anyone can be at risk of heat stroke, certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. It is important to be aware of these risk factors in order to take appropriate precautions and protect yourself from heat stroke. Vulnerable Groups Certain groups of people are more vulnerable to heat stroke than others. These include: 1. Elderly individuals: Older adults have a reduced ability to adjust to changes in temperature, making them more susceptible to heat stroke.
Mild Heat Stroke Symptoms NHS
Additionally, they may have underlying health conditions that further increase their risk. 2. Children: Young children are at a higher risk of heat stroke due to their smaller bodies and higher metabolic rates. They may also be less aware of the signs of overheating and may not be able to communicate their discomfort effectively. 3. Individuals with chronic medical conditions: People with conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and respiratory disorders are more prone to heat stroke. These conditions can impair the body’s ability to cool down and increase the risk of heat-related complications. Environmental and Lifestyle Triggers Environmental and lifestyle factors also play a significant role in heat stroke risk.
Mild Heat Stroke Symptoms NHS
Some of the key triggers include: 1. High temperatures and humidity: Exposure to extreme heat and humidity increases the risk of heat stroke. This is particularly true in hot climates or during heatwaves, where the body may struggle to dissipate heat effectively. 2. Strenuous physical activity: Engaging in intense exercise or laborious work in hot conditions can lead to rapid overheating and increase the risk of heat stroke. It is important to take regular breaks, stay hydrated, and avoid exertion during the hottest parts of the day. 3. Lack of hydration: Inadequate fluid intake can impair the body’s ability to regulate temperature and cool down. Dehydration makes it harder for the body to sweat, which is a crucial cooling mechanism.
Mild Heat Stroke Symptoms NHS
4. Certain medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, antihistamines, and stimulants, can affect the body’s ability to cool down and increase the risk of heat stroke. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional regarding the potential side effects of medications in hot environments. Taking precautions to prevent heat stroke is essential, particularly for those at higher risk. It is important to stay hydrated, seek shade or air-conditioned environments, and limit outdoor activities during the hottest parts of the day. By understanding the risk factors and implementing appropriate measures, you can protect yourself and others from the dangers of heat stroke.
Preventative Measures
When it comes to preventing mild heat stroke, taking the right precautions is key. Here are some essential strategies to help you stay safe and cool during hot weather:
Hydration Strategies
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption.
- Consider electrolyte-rich beverages for added hydration.
Appropriate Clothing Choices
- Wear lightweight and breathable fabrics.
- Opt for light-colored clothing to reflect sunlight.
- Choose loose-fitting garments to promote air circulation.
First Aid For Heat Stroke
Mild heat stroke symptoms, according to NHS guidelines, include dizziness, headache, and feeling nauseous. It’s vital to stay hydrated and seek shade to prevent heat-related illness. Cooling measures like cold packs can help alleviate discomfort.
Heat stroke is a serious condition that requires immediate attention and proper first aid. When someone is experiencing heat stroke, it is crucial to take immediate actions and employ cooling techniques to lower their body temperature. Here are the steps to provide first aid for heat stroke:
Immediate Actions
The first and foremost step is to call for emergency medical assistance. While waiting for help to arrive, it is important to move the affected person to a cooler and shaded area. This helps to prevent further exposure to heat and allows for better temperature regulation. Lay the person down and elevate their legs slightly to improve blood flow to the brain. Loosen any tight clothing and remove unnecessary layers to aid in the cooling process.
Cooling Techniques
Cooling the body is crucial to prevent further damage from heat stroke. Here are some effective cooling techniques to help lower body temperature: 1. Apply cool water: Wet a cloth or sponge with cool water and gently apply it to the person’s skin. Focus on areas with high blood flow, such as the neck, armpits, and groin. This helps to promote rapid cooling. 2. Use a fan: If available, use a fan to increase air circulation around the affected person. This aids in the evaporation of sweat, which helps to cool the body.
3. Mist with water: Spraying a fine mist of water on the person’s skin can also aid in the cooling process. This can be done using a spray bottle or a misting device. 4. Ice packs or cold compresses: Apply ice packs or cold compresses to the person’s neck, armpits, and groin to lower their body temperature. Be sure to wrap the ice packs or compresses in a cloth to prevent direct contact with the skin.
Remember
It is important to continuously monitor the person’s condition while providing first aid for heat stroke. If their symptoms worsen or they lose consciousness, be prepared to perform CPR if necessary. Heat stroke is a medical emergency, and swift action can make a significant difference in the person’s recovery. Stay vigilant and prioritize their well-being until medical professionals arrive. Remember, prevention is always better than cure. Stay hydrated, avoid excessive heat exposure, and take breaks in cool and shaded areas to prevent heat stroke from occurring in the first place.
Long-term Health Implications
Mild heat stroke symptoms can have long-term health implications, according to the NHS. It is important to recognize and treat these symptoms promptly to prevent potential complications.
Potential Complications
Long-term health implications of mild heat stroke can be severe and potentially life-threatening if not treated promptly. When left untreated, the condition can lead to a range of complications, including:
- Heat exhaustion
- Heat cramps
- Dehydration
- Heat edema
- Heat rash
- Heat syncope
These complications can occur due to the body’s inability to regulate its internal temperature, leading to an increase in core body temperature and resulting in damage to vital organs.
Recovery And Monitoring
Recovery from mild heat stroke depends on the severity of the condition and how quickly it is treated. In most cases, patients can recover fully with proper rest, hydration, and cooling measures. However, it is important to monitor the patient closely for any signs of worsening symptoms or complications.
If left untreated, mild heat stroke can progress into a more severe form of heat stroke, which can cause irreversible damage to the brain, heart, kidneys, and liver. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of mild heat stroke. In conclusion, mild heat stroke can have long-term health implications if not treated promptly. It is important to recognize the symptoms of heat stroke and take appropriate measures to prevent the condition from worsening. Remember to stay hydrated, avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, and seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of heat stroke.
Educating The Public
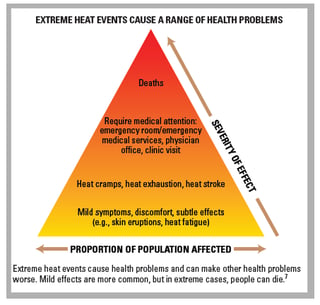
Education is paramount in preventing and managing mild heat stroke symptoms. By raising awareness and fostering community support, we can equip the public with the knowledge and resources to address this health concern effectively.
Awareness Campaigns
Engaging in awareness campaigns can help disseminate essential information about mild heat stroke symptoms. Through various media platforms, including social media, television, and community events, individuals can access valuable insights on recognizing and responding to heat-related health issues.
Community Support Initiatives
Implementing community support initiatives, such as distributing informational pamphlets, organizing workshops, and collaborating with local healthcare providers, can empower communities to take proactive measures in addressing mild heat stroke symptoms. By fostering a network of support and knowledge, individuals can better protect themselves and their loved ones from the risks associated with heat-related illnesses.
Credit: info.isabelhealthcare.com
Nhs Guidelines And Resources
When it comes to managing mild heat stroke symptoms, it’s crucial to be aware of the official guidelines and resources provided by the NHS. Understanding the recommended steps and knowing where to access help and information can make a significant difference in addressing this condition effectively.
Official Recommendations
The NHS offers clear and comprehensive guidelines for recognizing and managing mild heat stroke symptoms. These official recommendations provide valuable insights into identifying the signs of heat-related illness and taking appropriate action to prevent the condition from escalating.
Accessing Help And Information
Accessing help and information regarding mild heat stroke symptoms is vital for ensuring prompt and effective assistance. The NHS provides accessible resources, including online information, helplines, and local healthcare services, to support individuals in need of guidance or medical attention.
Credit: www.nhs.uk
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Treat Mild Heat Stroke?
Treat mild heat stroke by moving to a cooler place, resting, and hydrating with water. Remove excess clothing and use cool compresses. If symptoms worsen, seek medical help.
How Do You Know If You Have Mild Heat Stroke?
Symptoms of mild heat stroke include headache, dizziness, nausea, and muscle cramps. You may also experience excessive sweating and a rapid heartbeat. If you suspect heat stroke, seek shade, hydrate, and cool your body. If symptoms persist, seek medical attention.
How Quickly Does Heat Stroke Set In?
Heat stroke can set in quickly, often within 10-15 minutes of exposure to high temperatures. Symptoms may include a high body temperature, headache, dizziness, nausea, and confusion. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you suspect heat stroke.
How Long Does It Take For Heat Exhaustion To Go Away?
It typically takes a few hours for heat exhaustion symptoms to go away with proper rest and hydration.
Conclusion
Recognizing mild heat stroke symptoms is crucial for timely intervention. By understanding the signs like excessive sweating, dizziness, and fatigue, one can prevent serious health complications. Stay vigilant, stay hydrated, and seek medical help if you experience any symptoms to stay safe in the heat.
